Tesla faces significant sales decline in European markets
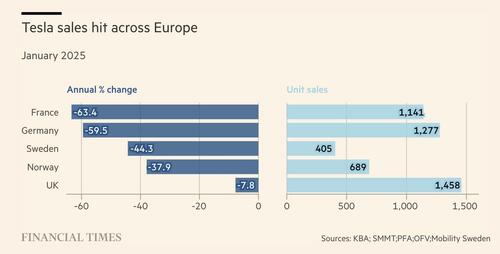
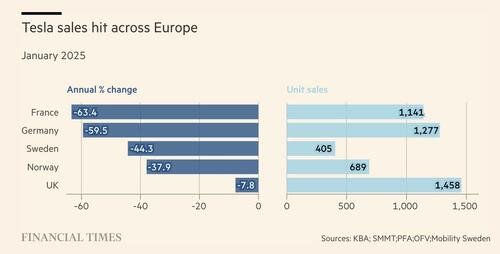
The start of 2024 has proven challenging for Tesla in Europe, with the latest sales data showing a significant decline in key markets. According to a recent report, Tesla’s vehicle registrations in Germany fell by a staggering 59.5% in January compared to the same month last year. This drop is particularly concerning given that Germany is home to Tesla’s only European production facility, the Berlin-Brandenburg Gigafactory.
The downturn isn’t isolated to Germany. Other major European markets also saw a dip in Tesla sales during January. In France, sales declined by an even sharper 63%, while Norway, one of the most EV-friendly nations in the world, reported a 38% drop. The United Kingdom saw a more modest decline of 8%, but the downward trend remains evident across the region.
These figures come despite the overall European EV market witnessing steady growth. In Germany, electric vehicle sales surged by over 50% year-over-year, yet Tesla’s market share tumbled from 14% to just 4%. This stark contrast suggests that while demand for EVs remains strong, competitors may be capturing a larger share of the expanding market.
While Tesla remains a dominant force in the global EV industry, the recent sales slump raises questions about whether shifting consumer preferences, emerging rivals, or other external factors are beginning to impact its position in Europe. With other automakers intensifying their EV efforts and local subsidies influencing buying behaviors, Tesla’s path forward in the European market may require strategic adjustments.
Several factors appear to be contributing to Tesla’s recent drop in sales across European markets. One major reason could be the phasing out of government subsidies in key countries like Germany and France. Historically, these subsidies played a crucial role in incentivizing EV purchases, and their reduction or removal may have shifted consumer demand toward more affordable alternatives. Buyers who previously relied on financial incentives to justify a Tesla purchase may now be exploring lower-cost EVs from competing brands.
Another significant factor is a potential shift in consumer sentiment regarding Elon Musk. Tesla’s outspoken CEO has been a polarizing figure, and his political statements and social media activity have not gone unnoticed in the European market. Some analysts speculate that Musk’s vocal involvement in geopolitical discussions and controversial topics has alienated a portion of European consumers, particularly in Germany. The country has a keen focus on sustainability, progressive policies, and social responsibility, and any perceived misalignment with those values could be impacting Tesla’s appeal.
Additionally, the anticipation of new Tesla models may also be contributing to the slowdown. With news that an updated Model Y is expected in 2025, some potential buyers may be delaying their purchases, opting to wait for the refresh rather than invest in the current version. This pattern has been observed before with Tesla vehicles, as buyers hold off in anticipation of technological or design improvements.
Competition in the EV market is also fiercer than ever. European and Chinese automakers are rapidly expanding their EV offerings, with models that boast competitive pricing, advanced technology, and localized manufacturing advantages. Brands like Volkswagen, BMW, and BYD are gaining traction in key Tesla markets, offering strong alternatives for consumers who may be looking beyond Tesla for their next EV purchase. The increased variety in choices means Tesla is no longer the default option for those seeking an electric vehicle.
Lastly, supply chain disruptions and production constraints cannot be ignored. While Tesla continues to ramp up operations at its Berlin Gigafactory, logistical challenges and component shortages may be impacting the company’s ability to meet demand efficiently. If potential customers face long wait times for deliveries or see inconsistent availability, they may turn to competitors that can fulfill orders more quickly.
Given all these variables, Tesla’s European sales decline is likely influenced by a combination of external market dynamics, evolving consumer preferences, and internal company challenges. Whether these factors are short-term fluctuations or indications of a larger shift remains to be seen, but for now, Tesla faces an increasingly competitive landscape in a region that was once a major stronghold.
The European EV market is evolving at a rapid pace, and while Tesla has long been the dominant player, competition is intensifying like never before. In recent years, both European and Chinese automakers have been aggressively pushing into the space, offering a diverse range of electric models that are attracting a growing number of buyers. With Tesla’s recent sales decline in key markets, it’s clear that the brand is facing strong headwinds from an expanding pool of competitors.
One of the biggest challenges Tesla is encountering is the rise of homegrown European automakers that are capitalizing on their familiarity with regional consumer preferences. Established giants like Volkswagen, BMW, and Mercedes-Benz have significantly ramped up their EV production, launching models that cater to local tastes and offer pricing structures that benefit from European manufacturing incentives. Volkswagen’s ID series, for example, has been particularly successful in attracting customers who may have once considered a Tesla but now find better value and availability in Volkswagen’s expanding lineup.
Chinese EV manufacturers are also making their presence felt in Europe. Brands such as BYD, Nio, and Xpeng are increasing their footprint in the region, bringing competitive models that often boast impressive technology and lower price points. BYD, in particular, has aggressively expanded into the European market, introducing vehicles that rival Tesla in range and performance but at a significantly lower cost. The affordability of these Chinese EVs is reshaping consumer choices in markets where price plays a crucial role in purchasing decisions.
Another key development in the broader EV market is the increased focus on affordability. With the removal of subsidies in some countries, automakers are adjusting their strategies by launching more budget-friendly EVs. Tesla, despite its continued dominance in premium electric vehicles, has not yet introduced a true low-cost electric car for the European market. Meanwhile, competitors are filling this gap with models that offer solid features at a fraction of Tesla’s prices. Dacia’s Spring, for example, has gained traction as one of the most affordable fully electric cars in Europe, providing consumers with a practical and economical alternative.
Additionally, the shift toward hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles is influencing the broader EV market. While full battery electric vehicles (BEVs) remain the long-term focus for many automakers, hybrids still play a crucial role in the transition to electrification. Some consumers, perhaps hesitant about charging infrastructure or range limitations, are opting for plug-in hybrids from brands like Toyota and Peugeot instead of committing to a full EV. This shift could be siphoning away potential Tesla buyers who are seeking flexibility in their vehicle choices.
Charging infrastructure is also a major talking point in the ongoing EV transition. While Tesla continues to expand its Supercharger network across Europe, governments and competing automakers are investing heavily in universal charging solutions that are more inclusive for all EV brands. Audi, BMW, and several other manufacturers have teamed up to deploy high-speed charging stations, ensuring that Tesla’s once-clear advantage in charging infrastructure is no longer a major selling point. As more automakers embrace standardized fast-charging networks, the exclusivity of Tesla’s Superchargers may become a less compelling reason for consumers to choose a Tesla over another brand.
The competitive pressures on Tesla are mounting, and the next few years will be critical in determining whether the company can maintain its leadership in the European EV market. With rivals advancing in affordability, innovation, and manufacturing efficiency, Tesla will need to adapt quickly to meet shifting demands. Whether that means accelerating the arrival of its long-promised cheaper model or finding new ways to differentiate itself in an increasingly crowded field, the automaker’s ability to navigate these challenges will dictate its position in the region moving forward.
The turbulence surrounding Tesla’s European sales has understandably sparked significant reactions from investors, analysts, and consumers alike. With stockholders closely watching each development, the decline in sales and shifting market dynamics have raised questions about Tesla’s immediate future in the region. The reactions have been mixed—some see these figures as a temporary setback, while others view them as early warning signs of deeper challenges ahead.
Notably, Tesla’s stock has faced periods of volatility following the release of these sales figures. Some investors remain optimistic, pointing to the company’s ability to innovate and adjust to changing market conditions. Supporters argue that Tesla’s historical resilience and brand loyalty will help it weather this temporary downturn, particularly as it prepares to refresh its key models like the Model Y and continues to push advancements in autonomous driving technology. Others highlight that even with the recent dip, Tesla remains one of the most well-recognized and trusted names in EVs, and that brand equity continues to have significant value in the long run.
On the other hand, skeptics warn that if Tesla does not take rapid and strategic action, it risks losing its foothold in an increasingly competitive European market. With companies like Volkswagen, BYD, and BMW offering compelling alternatives, Tesla’s ability to maintain its momentum is no longer guaranteed. Some analysts have pointed out that while Tesla’s cars remain technologically advanced, competitors are catching up fast, offering vehicles with similar capabilities at lower price points—something that could continue to erode Tesla’s market share if unchecked. Additionally, concerns around Elon Musk’s controversial public persona and its potential impact on consumer sentiment, particularly in European markets, remain a topic of discussion among industry experts.
Looking ahead, Tesla has several strategic opportunities that could help it rebound in the European market. The upcoming refresh of the Model Y, expected sometime in 2025, could help revive interest, particularly if it introduces new features and enhancements that differentiate it from the competition. Additionally, Tesla’s long-promised affordable EV—potentially a “Model 2” or a similar budget-friendly offering—could be a game-changer if launched at the right price point. Europe’s shift toward more cost-conscious EV buyers means Tesla will need to address this demand if it hopes to sustain long-term success.
Another factor to watch is the regulatory landscape across Europe. As governments continue pushing for stricter emissions targets and greater EV adoption, Tesla may find new opportunities to expand—especially if additional incentives or infrastructure commitments emerge that align with Tesla’s plans. However, the company must also navigate regulatory challenges, including any potential shifts in trade policies, localization requirements, and ongoing geopolitical considerations that could impact supply chains and production efficiency.
Despite recent setbacks, Tesla remains a dominant force in the EV market. Whether it can maintain its stronghold in Europe depends on how well it adapts to evolving consumer preferences and rising competition. The coming months will be telling, as Tesla faces a critical period where operational decisions, product refreshes, and broader market strategy will determine whether this sales decline is a short-term hurdle or an indication of more fundamental challenges for the company’s European ambitions.